TOPIC: Rocket fuels and propellants
Objective: To demonstrate how increasing the surface area of a chemical increases its reaction rate.
Description: A whole antacid tablet and a crushed tablet are added to separate beakers of water so that their relative reaction rates can be compared.
EDITED BY: Roger Storm, NASA Lewis Research Center
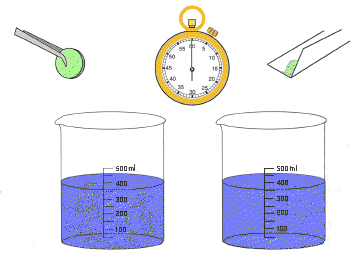
Discussion: This activity demonstrates how increasing the surface area of an antacid tablet by crushing it into a powder increases the rate in which it dissolves in water. This is a similar situation to the way the thrust of a rocket is increased by increasing the burning surface of its propellants. Increasing the burning surface increases its burning rate since more fuel becomes exposed to oxygen . In solid rockets, a hollow core extending the length of the propellant will permit more propellant to burn at a time. This increases the acceleration of the gases produced as they leave the rocket engine. Liquid propellants are sprayed into the combustion chamber of a liquid propellant rocket to increase their surface area. Smaller droplets react more quickly than do large ones, increasing the acceleration of the escaping gases.
![]() EVOLUTION OF CARBON DIOXIDE LAB A chemistry lab
EVOLUTION OF CARBON DIOXIDE LAB A chemistry lab
GO
BACK TO THE ROCKET ACTIVITIES
Aerospace Education Services Project Oklahoma State University